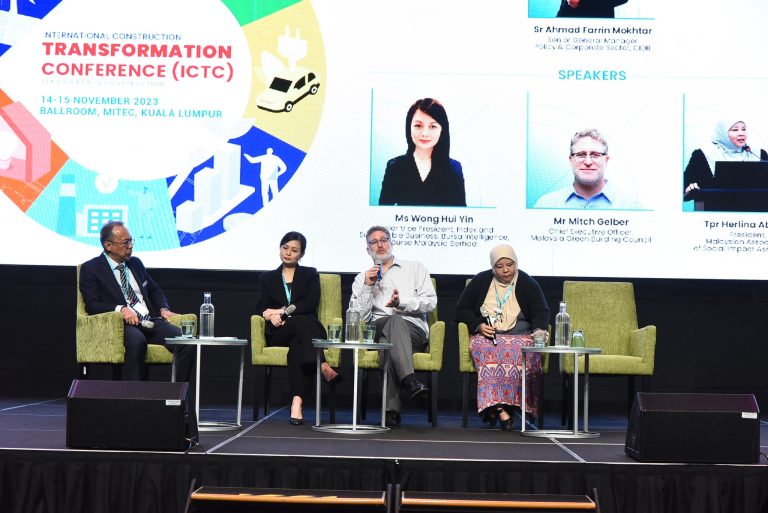
As Malaysia strives to usher in a new era of environmental responsibility, CEO of Malaysia Green Building Council (MalaysiaGBC), Mitch Gelber, explains how their innovative CarbonScore’s annual assessment tool is a crucial catalyst towards transitioning the existing buildings to net zero carbon, at the International Construction Transformation Conference (ICTC) 2023 session in MITEC, Kuala Lumpur.
It is becoming a global movement for the construction sector to strive for net zero in buildings. Striving for a greener nation, 95% of new construction projects in Malaysia are certified green buildings.
Furthermore, the Malaysian government believes it is time to take action and thus formulated the National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR) and Malaysia Energy Transition Outlook as clear guidelines for all sectors to follow closely.
Mitch states that as the future focuses on lower energy costs and reduced carbon footprint, Malaysia must transform its energy landscape, which is currently heavily reliant on fossil fuels and tap into the significant potential of renewable energy sources.
Source: www.IEA.org 4th Biennial Update Report to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
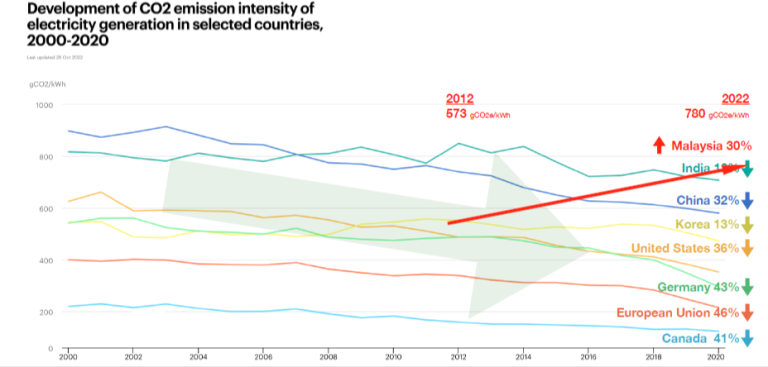
According to the Malaysia Energy Transition Outlook, renewable energy presents a more economical alternative to fossil fuels. The report forecasts that the proportion of renewable energy in the country’s final energy mix will surpass 50% by 2050, a significant increase from the current 5%.
To reshape the construction landscape and fast-track the nation’s journey towards a greener, more sustainable future, CarbonScore works to assess the whole-life CO2 emissions for existing buildings. It evaluates a building’s contributing factors of CO2 footprint, such as operational carbon, mainly from electricity consumption, embodied carbon associated with the materials and manufacturing process, and reduced emissions via energy efficiency.
The environmental toll of buildings on a global scale cannot be overstated. Mitch reveals that buildings, globally, are responsible for around 40% of energy and process-related CO2 emissions and 50% of all extracted materials.
For Malaysia to reduce operational carbon for existing buildings, CarbonScore further suggests several pathways to take upon, which are energy efficiency maintenance, solar PV installation and purchasing renewable energy from the grid.















